Welcome to the comprehensive guide to build RESTful CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) API using the powerful trio of Node.js, Express.js, and mongoDB.
- Node.js: Node.js is a runtime environment that allows developers to execute JavaScript code server-side, enabling the building of fast and scalable network applications.
- Express.js: Express.js is a web application framework for Node.js that simplifies the process of building web applications and RESTful APIs by providing a robust set of features and middleware.
- MongoDB: MongoDB is a NoSQL database that uses a document-oriented data model, making it flexible and scalable for storing and managing structured and unstructured data in modern applications.
Github Link for Source Code of CRUD API : https://github.com/arjungautam1/Express-CRUD
Step 1 : Create project and install npm packages
First, create a folder let’s call it crud and open it any code editor. I will use VSCode for this tutorial; you can use any code editor like WebStorm or Atom. Now Open the terminal in VSCode, then type:
npm init
Keep everything as default or you can provide some fields like author or description. If you keep on pressing enter this will create a file called package.json.
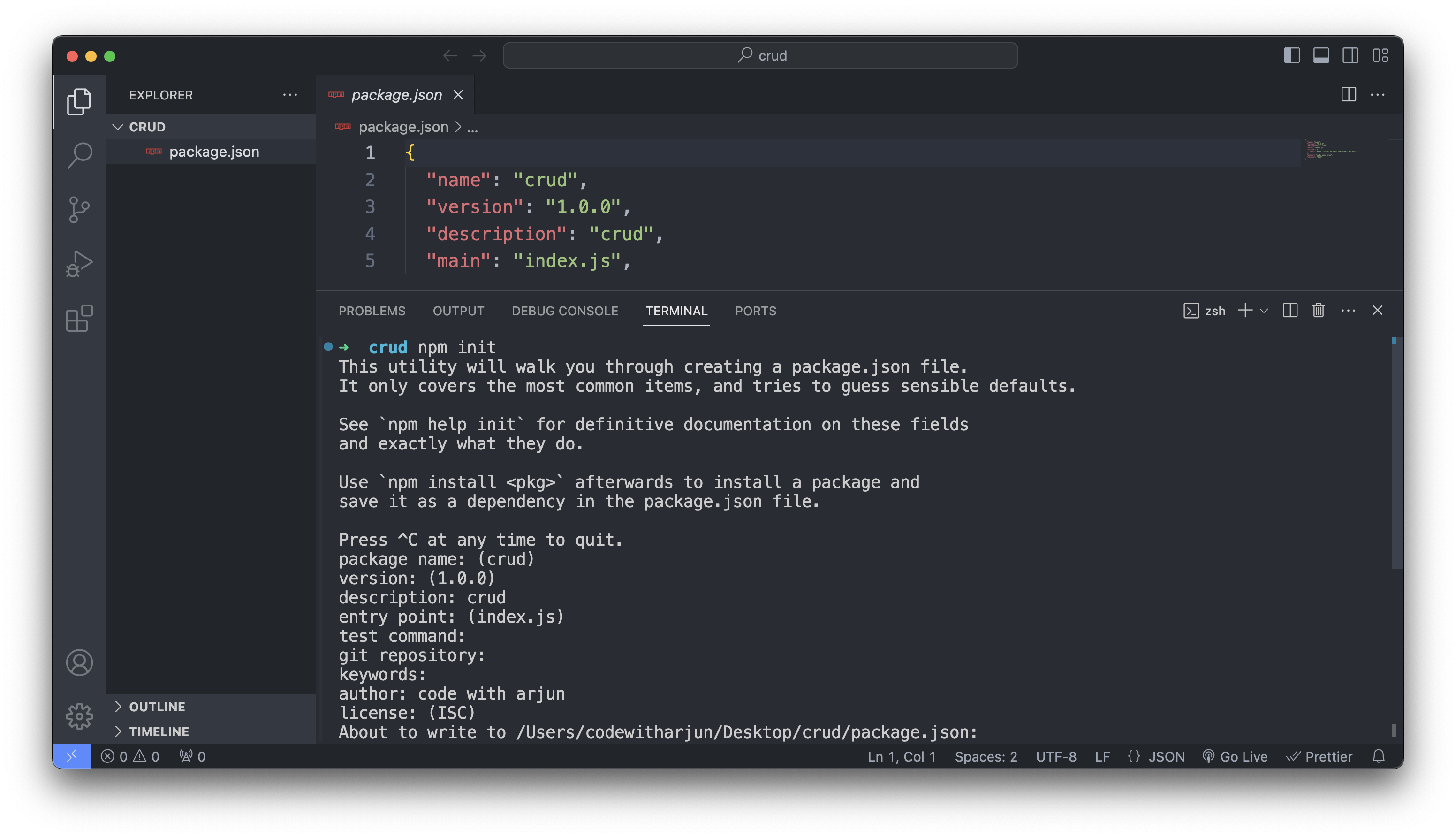
Now install npm packages : body-parser for parsing incoming request bodies in middleware functions, dotenv for loading environment variables from a .env file, and express for creating web applications and APIs in Node.js. mongoose for modeling and interacting with MongoDB databases in Node.js applications, providing a schema-based solution for organizing data and facilitating CRUD operations with ease.For that type the following command on terminal :
npm i express dotenv body-parser mongoose
Also install Nodemon as dev dependency : Nodemon is a utility that monitors changes in your Node.js application files and automatically restarts the server upon detecting modifications, facilitating a streamlined development workflow.
npm install --save-dev nodemon Now let’s some changes on package.json : add type: “module” just below main:”index.js” and change start:”nodemon index.js” inside scripts as shown below
Step 2 : Create database using MongoDB Compass
First make sure to install monogoDB and mongoDB Compass on your operating system. If you haven’t installed yet I have dedicated video for the installation first go through these video to install :
Install MongoDB and mongoDB Compass on Windows : https://youtu.be/jvaBaxlTqU8
Install MongoDB and mongoDB Compass on Mac : https://youtu.be/MyIiM7z_j_Y
Install MongoDB and mongoDB Compass on Linux (Ubuntu) : https://youtu.be/ZiQPyD82ojk
Once you install mongoDB and mongoDB Compass create database using mongoDB compass. Let’s call it crud and give the collections name users. I also have dedicated blog on this topic.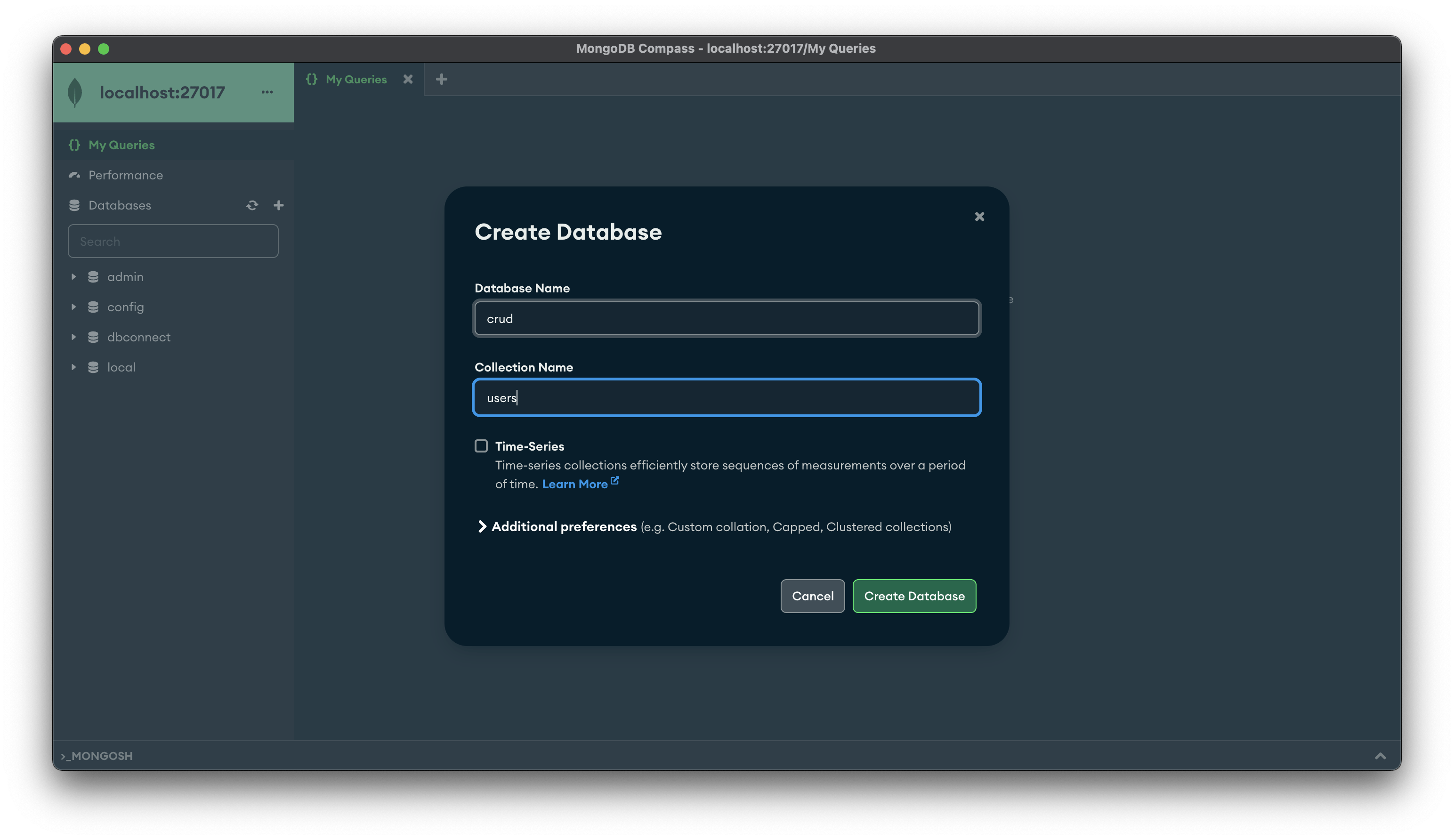
Now let’s create .env in the crud folder to add the database configuration and port.
Step 3 : Connect express.js with mongoDB
Now create a index.js file and here will write code to connect express.js with mongoDB database in following steps :
- Import necessary modules
- Initialize Express app
- Create Middleware for parsing JSON request bodies
- Load environment variables from .env file
- Write code for Connecting MongoDB database
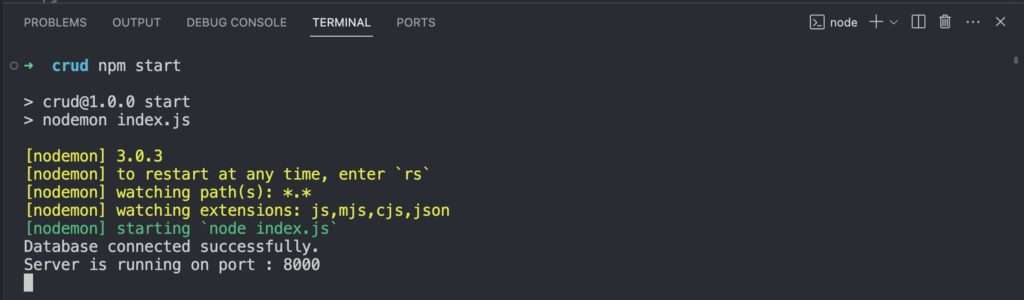
Now if you type npm start in terminal you will see the message database connected successfully and server is running on port :8000
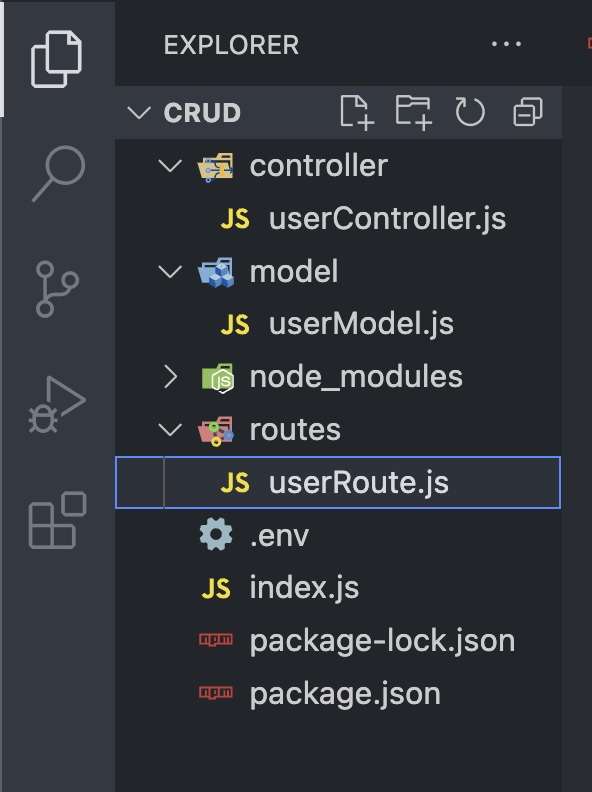
Now create the folder structure:
- model -> userModel.js for defining the schema and model for the user data in MongoDB.
- controller -> userController.js for handling the business logic and interaction with the userModel.
- routes -> userRoute.js for defining the routes and mapping them to the appropriate controller methods for user-related operations.
Step 4 : Create Model or userSchema
Now create user schema with properties name, email and address. Then create and export the Mongoose model for the “users” collection based on the userSchema.
Step 5 : Create UserController
Now Let’s write code for controller file. It receives HTTP requests from the routes defined in userRoute.js, such as requests to create, read, update, or delete user data.
- First import userModel.js as User
- Then write code for posting data into database, getting all the users from database, then for updating the data from database and deleting the data from database.
Step 6 : Create User Routes
Now let’s write code for userRoute.js, which is for defining the routes and mapping them to the corresponding controller functions for user-related operations.
- First import the express module
- Then, import controller functions for handling user routes
- Create a new router instance
- Define routes and their corresponding controller functions
- Export the router
Now just add these lines in index.js file:
Line number 7 [import route from “./routes/userRoute.js”;] &
Line number 28 [app.use(“/api/user”, route); ]
Now your application should be running successfully.
Now just install Postman to check all the API endpoints. If you haven’t installed the postman. Download it and install on your system from this link: https://www.postman.com/
Now open Postman and start testing all the API endpoints. First let’s test POST HTTP method to insert into database.
Step 7 : Test API using Postman
- First Create a New POST Request
- Then put URL : http://localhost:8000/api/user/create
- Then choose Body -> raw ->json
- And Write the json of name, email and address
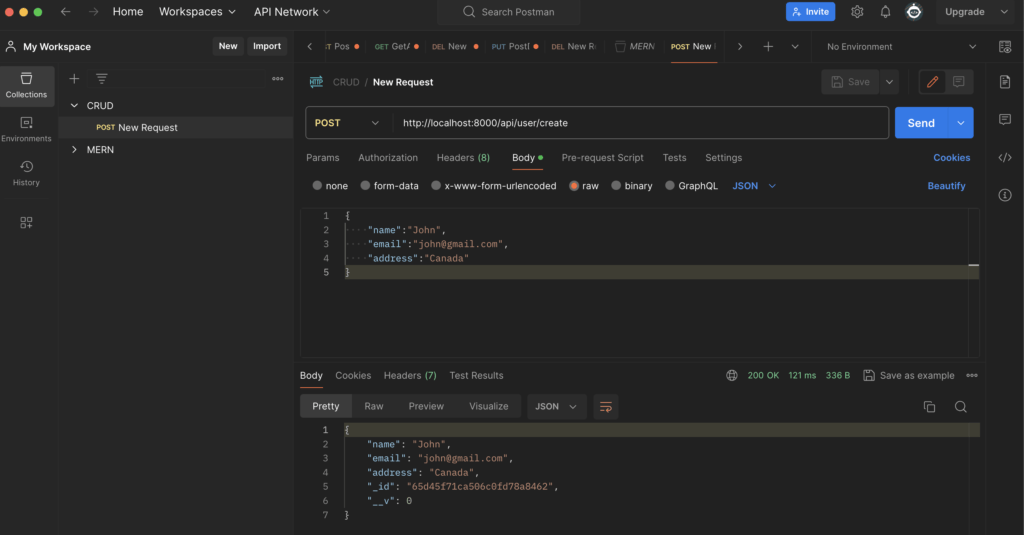
{
“name”:”John”,
“email”:”john@gmail.com”,
“address”:”Canada”
} - Now just press on Send and see the Body there is same json
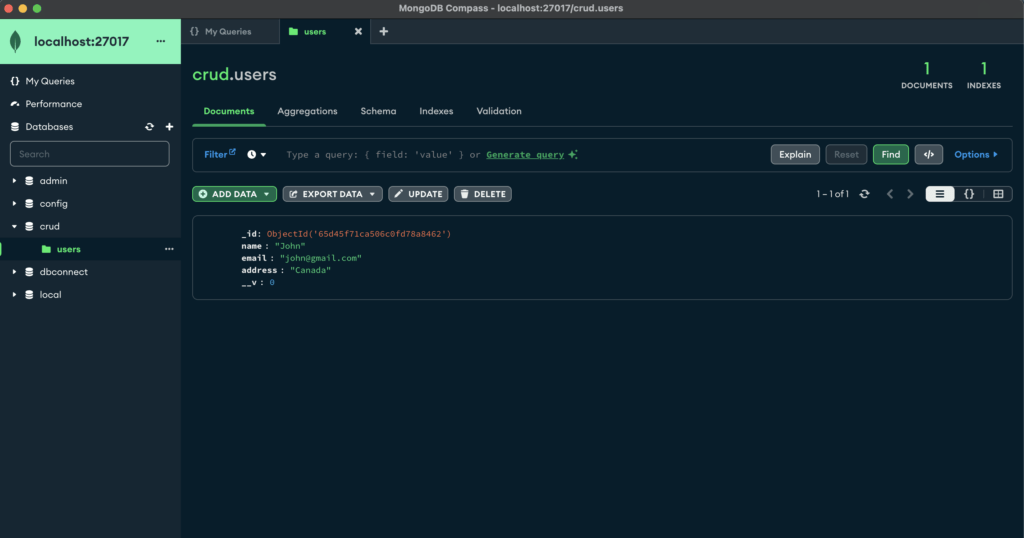
Now check the database you will see the data in users collection.
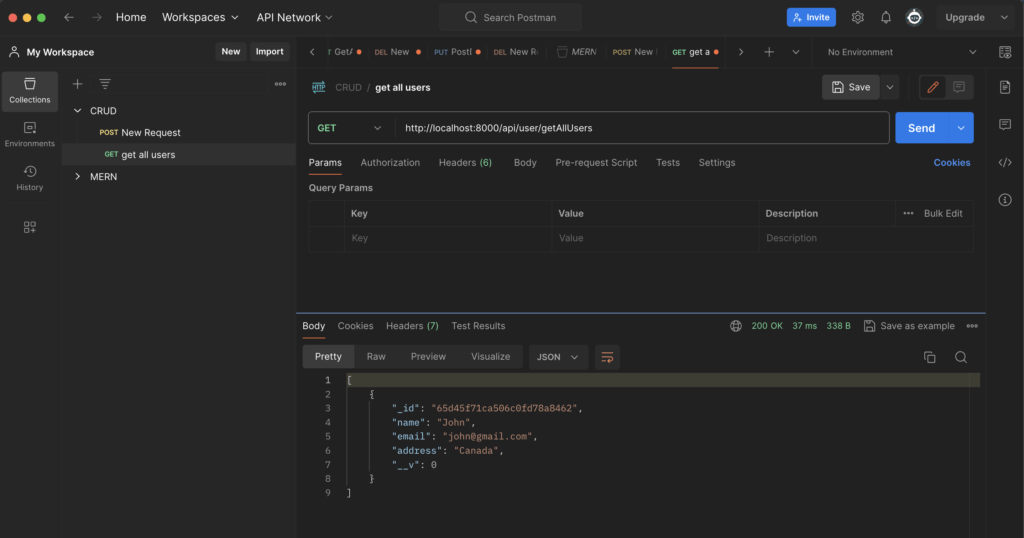
Now Let’s test the GET API endpoint for getting all data from database
For that, Just select GET method and provide the URL http://localhost:8000/api/user/getAllUsers
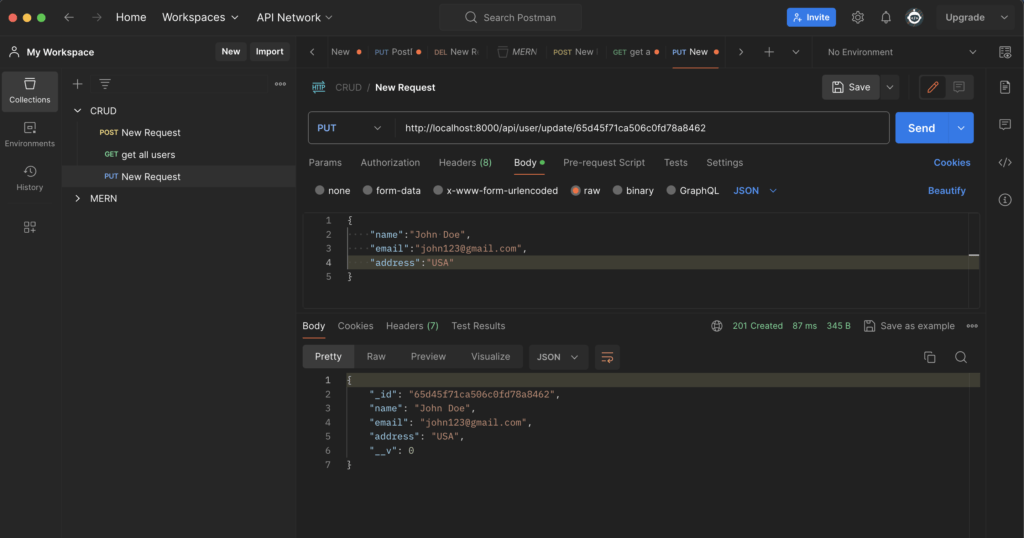
Now let’s update data from database using PUT method provide URL
- First Create a New PUT Request
- Then put URL : http://localhost:8000/api/user/update/id
- Then choose Body -> raw ->json
- And Write the json of name, email and address
{
“name”:”John Doe”,
“email”:”john123@gmail.com”,
“address”:”USA”
} - Now just press on Send and see the Body there is same json
Now For deleting data from data you can just add the new DELETE request and API endpoint : http://localhost:8000/api/user/delete/id
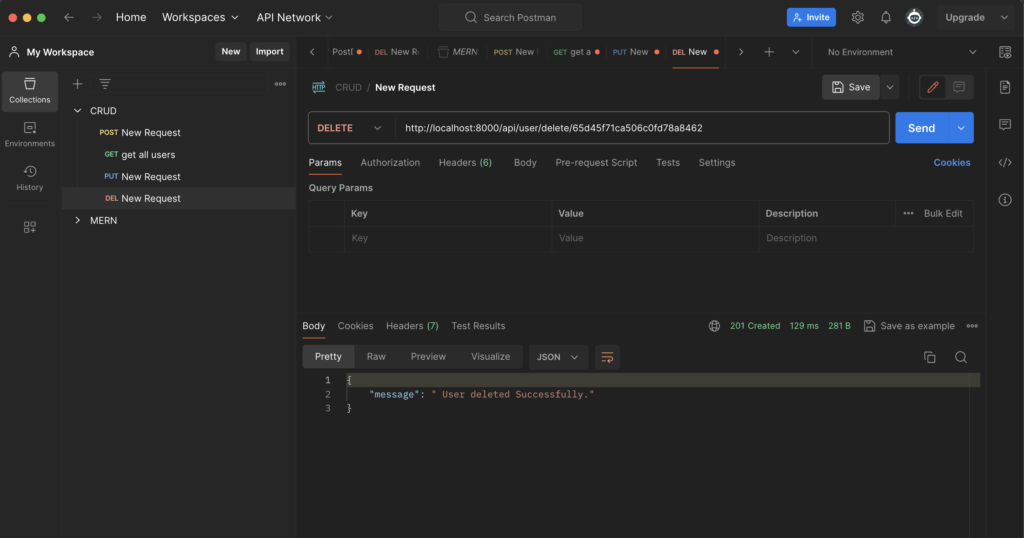
If data is deleted successfully. It will show the message
{“message “: “User deleted successfully”}

